How SEO works
The first and important rule in search engine optimization is to offer value, but it is subject to feelings and emotions, therefore – it is always biased. To rank well within the search engine – you need to give a clear indication that your pages are better than your competitors. There are a lot of strategies, tactics and best practices to achieve this, but the most important thing you can do – optimize your content, make sure you have everything you need and control is simply excellent. Also, remember that search engines will rank the most relevant pages the most important. This means that, for a search query, they will first take a set of relevant pages and then display them in the result pages according to their importance and notoriety.
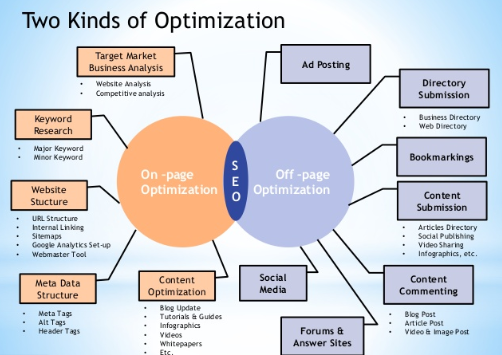
On-page optimization workflow
On-page SEO is about creating or increasing the relevance signal for a webpage in relation to search queries. Having some experience in optimizing and promoting websites, we were able to reduce some of the rules that are required and which helped us prioritize our work process and enhance our results. We hope that these rules will also help you.
Keyword research
Before you start writing any content (including title, meta description, image name, etc.), you should know what the problem you are trying to solve is – the people who are really looking for And which expressions have the highest search volume. You should also keep the competition in mind and choose the right balance between the most searched keywords and those with less competition.
You can do this research using a lot of tools, but the most popular are those offered by Google (Search, Analytics, Webmaster Tools, AdWords, Trends).
When analyzing the competition – start by googling for super-keywords and pay attention to their titles, meta descriptions, URLs and headlines and then be sure to create better versions. Having great URLs, titles and descriptions is extremely important, as these are the things that make a snippet of search engine results.
Rule #1
A webpage should be tailored around just one family of keyword
One Super-keyword
It should be optimized around a keyword (called a super-keyword), and all linked keywords (variations, synonyms, etc.) that will be related to each other.
Good text amount
This is the page you want to rank with all the search queries in the same family, so you need a good amount of text that covers the topic well.
A keyword family
Relevance signals should include keywords in the target family, also known as “keyword cannibalism,” to avoid competition in targeted pages only
Rule #2
Use keyboard variation (instead of just the super keyword) in a prominent location
The use of keyword variation is low-risk (due to the “over-optimization” penalty). This will help you cover more semantic fields (more long-tailed keywords). Also, it is good to know that long terms are better than short terms (if we like it it would be easier to rank for super-keywords).
Keeping the above in mind, it is important to prioritize keywords (based on their estimated search volume).
URL
The URL address should describe the page as closely as possible. Users should be able to understand if the page will meet their needs without loading it into their browser. The URL address suffix (including the last part, domain name, or parent folder) should be the shortest summary of the page. The URL address prefix (domain name + parent folder) should provide the reference.
Try to meet the following requirements:
- Keep URL length below 100 characters
- Include super-keywords
- Separate words with dashes (-) instead of underscores (_)
- Be descriptive and memorable to the user
- Avoid keyword stuffing
- Avoid dynamic parameters (sortby, session, lat, lng, etc.)
- Avoid words without search capability (information, tags, articles, etc.)
- Avoid special characters (except languages like Russian, Chinese etc.)
- Make the URL shareable (no one should load the same content from where, from where or when to load it)
As a conclusion, we can deduce the following rule:
Rule #3
The URL is the shortest summary of the page
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is an address for a resource on the Internet. This element is important for on-page optimization.
Target keyword
The URL must contain the target keyword, which will be relevant and representative of all page content. It is recommended for a better crawl and better user experience. Always follow this rule!
Give accessibility
Right length
Of course, there are no definite rules, but you should keep the following factor in mind – a shorter URL is better than a long one because it is more accurate, natural and easier to remember.
Page Title
Your title tag appears at the top of the browser and as a title in the search engine result snippet. When a person shares that URL, social networks also use it as part of the post. For these reasons both its huge SEO value (this is one of the most important ranking factors), and “clickable” value (it serves as an incentive for people to click). You should try to find the right balance between excellent SEO and excellent user-friendliness.
some suggestions:
- Keywords must be close to the beginning
- Length between 50 and 60 characters
- must be unique
- Must be forced
- Use the brand name (at the end) only if it increases click-through)
- Avoid words without search capability
- Avoid keyword stuffing
- Avoid special characters (except languages like Russian, Chinese etc.)
- Make the URL shareable (no one should load the same content from where, from where or when to load it)
Keeping the above tips in mind, remember the next rule:
Rule #4
The title tag is the second shortest summary of the page
Title tags are the definitions of the document, which you can see in various places around the web, including tabs in your web browser. Those elements and are used to tell search engines and visitors what any page on your site is about.
Heading
Typically, they are implemented as HTML H1, H2 … H6 tags, but in fact nowadays search engines are getting better and better at interpreting CSS and JavaScript, so the heading is actually called something Can also be applied as. This is a classic scenario when size matters.
These are emphasized pieces of text (titles, subtitles, etc.) that show the most important “takeaways” to human visitors and search engines.
Spiders pay a lot of attention to the words used in titles, so they should always describe the content below correctly.
The H1 tag (the biggest title) should appear at the top-center of the b> page and the first thing people should see when they see it. It should be adapted as a “synonym” (rather than the same text) of the title tag, so – it includes super keywords or some close variants. There is no limit to the length, but they should not be too long and usually fit inside one or two lines.
Some suggestions: The headline should clearly communicate the subject of the page they are presenting.
Remember that page headlines are another reflection of your content.
Rule #5
The headline (H1) is the third shortest summary of the page
The title should be useful and informative, specific and relevant. Try to think beyond the traditional and make it unique and original.
Meta Description
The meta description is a summary of the page and appears as part of a search result snippet below the title of the page. It helps people decide whether to click on your site or other sites above or below it. Experiment until you get a satisfactory click-through rate.
Try to meet the following requirements:
- Length of 150–160 characters, but preferably no more than 156
- Super keyword once closer to the beginning and then some changes/synonyms, in an interactive format, user-friendly and easily understandable
- Provide valuable, compelling information for people to visit this page
- Must be unique within the domain (but also the entire WWW)
- Avoid keyword stuffing
Also, note that sometimes it is a good idea not to write a meta description at all, but it is subject to experiments. When the search engines do not get the description – they will generate one and use it inside that snippet. This is sometimes preferable because auto-generated descriptions use content fragments that contain search queries, thus making it relevant and compelling to the user. It is important to understand that search engines do not use meta descriptions as an SEO ranking factor. Sure. This only serves as an incentive for users to click on this search result, and not others so it doesn’t need to do stuff with keywords.
Meta Description Summary This is reflected by the following rule:
Rule #6
The Meta Description is the fourth shortest summary of the page
Meta description is an HTML attribute that provides a brief summary or explanation of page content. It is used on search engine result pages (SERPs) to display preview snippets for a given page. Even though this is not an important role for SEO, it is an important factor in user-friendliness. It should be compelling, highly informative and attractive to visitors.
Content
We can say that the content runs the site. Or that material is king. This is what eventually leads people to the website, keeps them happy, makes them share it and spreads the word.
The user searched for something, then reviewed the list of search results, analyzed URLs, titles and meta descriptions, etc., then decided to visit your page. Here’s when things get really interesting.
An important rule is to keep in mind that a user will spend 2 or 3 seconds to decide that what they have discovered is actually here. This is an important time frame and everything should be prepared before the user to make that decision easier.
The title is the first thing they will see. The first paragraph is the second and only then will they decide whether this page is good for their needs or not. If they bounce back on the search engine result page (“pogo-sticking”) – your ranking will suffer. If they live – the material still has to prove itself worthy.
There are no strict rules for writing great content, but there is a need to really make it great. One thing to remember though – Look and Feel should be designed in such a way that the user does not need to read every single content to get the original ideas. Instead – he or she should only be able to scan the page and easily remove the most important takeaways. As long as you need to read them and get ideas, you can achieve this by playing with headlines, bold text, internal table of contents, sorted or ordered lists of elements, etc.
Here are some tips and tricks:
- Te content for people, not for search engines
- Write at least several hundred words
- Make the first paragraph a summary of the page
- Place your targeted keywords at the beginning of the lesson
- Start content with text only, then feel free to add other formats as well
- Avoid flash banner
- Avoid ads
- Include at least one image to make the content friendly
- Add at least one link to another excellent page, especially if the visitor will get more details
- Unique value, provide relevant information, expand on the title, be interesting and informative for the potential visitor
- Keep the most important takeaways at the beginning and then expand on it
- People usually scan the page, so write short paragraphs that highlight only one idea
- Use super-keywords only 2 or 3 times throughout the page
- Use super-keyword variations and synonyms for a while
- Don’t worry about keyword density – just work on creating excellent copy
- Don’t do the same keywords, but keep in mind that the keywords will be indexed and bring traffic
- Include at least one list of ordered or unordered elements (instead of paragraphs or calculations), no more than 7-10 digits, shorten the list items – it helps people remember them.
- The group includes sub-headlines with paragraphs and important keywords.
- Initially include a table of contents, link to sub-headlines
- Use text in bold, italic, or underline to emphasize keywords and important ideas
- Check content for typos and spelling errors before placing your content on the page
We can reduce the following rules:
Rule #7
A webpage content should be unique and valuable
Obviously, it should stand on its own (valuable and different from other web pages) and easily solve the “problem” (provide information / answers, take action, etc.).
Basically, to achieve on-page SEO nirvana, you have to design the content in such a way that it becomes clear to anyone (both humans and bots) what they are. The way you can do this is to include the targeted locations in the key locations, ie – the areas in which users are most likely to pay attention:
Rule #8
The first paragraph is the fifth shortest summary of the page
Remember that the first paragraph is the main element that can catch the user’s attention. Build it carefully and think about your potential visitors – what do they expect from you? How can you convince them to read the following text and stay on your website?
Be original
The first paragraph is a mirror of the entire text and the bridge between you and your visitors. That is why, it must be unexpected, which will include phrases that will attract the attention of users and garner their sympathy.
Be clear
Obviously, people do not have time. This is why, the first words of your article or content should be very clear, concise and logically structured, so as not to complicate the user experience. Pay attention to it
Be relevant
Despite the desire to impress potential visitors by using a specific formula, the first paragraph should remain very relevant and informative, include a concise content plan and the most important keywords.
Rule #9
The body content is the longest summary of the page
We know you have heard it a hundred times, but if you have interesting, valuable, informative and funny texts, you will naturally attract traffic. Everything in SEO is based on this simple truth.
As mentioned above – search engines will first analyze their URLs, then titles, titles, descriptions and so on. Optimization is just making sure that these elements are very suggestive and accurately reflect your ranking intentions. Remember that you can always use an SEO checker to assess and help the quality of your content.
Images
All pages must have images as they are important in search ranking. They have the opportunity to show up in an image search, but they also regularly contribute to SEO. Having cheerful, good-looking pages and professional graphics can easily add a missing component to a user’s good experience.
Advanced search engines can also interpret texts within images, but hiding completely crawlable keywords inside them is not recommended. When optimizing, use the most important keywords for the first image, the next (synonyms, variations) for the second image, and the long-tailed keywords for the third.
Image optimization should meet the following requirements:
- Filename must match closely with URL suffix
- Separate keywords inside the filename with dashes (-)
- Use only lowercase characters in image file names
- Do not use special characters in the file name
- Be sure to use high-quality images
- Use the right resolution
- Make sure the image file size is as small as possible (use gif, png, jpg appropriately)
- Provide ALT attribute – optional text displayed by the browser when the image cannot be loaded; This should closely match the meta description
- Provide a TITLE attribute – the name of the image, it appears as a tooltip when the mouse is placed on the image; This should closely match the <title> tag of the page
Link
Links are very important for SEO. It is considered a good user experience to connect with other excellent resources that cover this topic further. They are usually (and always should be) highlighted within the text so that they ease the process of scanning through the document.
When optimizing links, consider the following best practices:
- Keep links low (<10)
- Only links to excellent resources
- Bold, italic or underscore if you want it to carry more weight
- Provide a TITLE attribute, it appears as a tooltip when the mouse is placed on the link and after clicking on the link the user should correctly (but briefly) describe the page they are about to land on.
- Use keywords with search capability as anchor text (not just the URL or “click here”)
- Use an absolute path to the referenced URL
- Do not use redirects for referenced URLs
- Do not use JavaScript or other techniques to produce links
- Avoid keyword stuffing in anchor text or title attribute
- Links to pages you want to rank highly
Speed optimization
The performance of your website remains and is a strong ranking factor and is something you need to focus on. Time and time again, Google has confirmed that websites that load faster are better than those that do not. In particular, it will become a strong ranking signal in the form of mobile search rankings.
Mobile connections are normally slow, thus websites not optimized for performance will have a tendency to load slower on mobile devices. Speed being the ranking factor also makes sense from a user point of view – a fast, fast website is a good user experience and user metrics have now become the core in rankings.
Slow websites also increase your bounce rate, which will negatively affect your ranking. If you want to optimize your website for speed, follow this easy (but detailed) guide on CollectiveRay, which is sure to speed up your website load.
What to do
- Optimize images for display (keep them small in size)
- Use a fast server like VPS to host your site
- Use a clean light weight theme
- Enable different caching mechanisms
- Do all possible technical optimizations